Methods and Interpretations
Skippy scores features for single nucleotide variants that were found to be significantly different in known splice-affecting variants (SAVs) that cause exon skipping when compared to coding polymorphisms from the HapMap project (which we refer for brevity as hSNPs), the vast majority of which are likely to have no effect on splicing. In addition to variants that cause exon skipping, Skippy can also be used to score putative SAVs that activate an ectopic splice site, as many of the same features are also relevant (albeit with different feature outcomes to look out for). These features are therefore to some degree predictive, although it is important to note that these features were identified by studying SAVs as a whole, and therefore not all SAVs share all the predictive features at once. Due to the complexity of exon definition and splicing, it is likely that some features are important in one context, while others may be important in others.
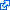
In addition to scoring inputted variants for these features, Skippy provides mean values from hSNPs for the same feature that are in similar genomic contexts (shaded in grey). In addition, to faciliate comparison, the variant feature is shaded if the value is considered to be significantly different from this mean in the direction associated with SAVs. This direction depends on the feature. For ease of reference, those features with values more similar to SAVs are shaded red and those less similar are shaded blue. The degree to which the values are shaded are meaured in Standard Deviations (S.Ds) from the hSNP mean.This allows the user to quickly scan for values that suggest a variant may be an SAV.